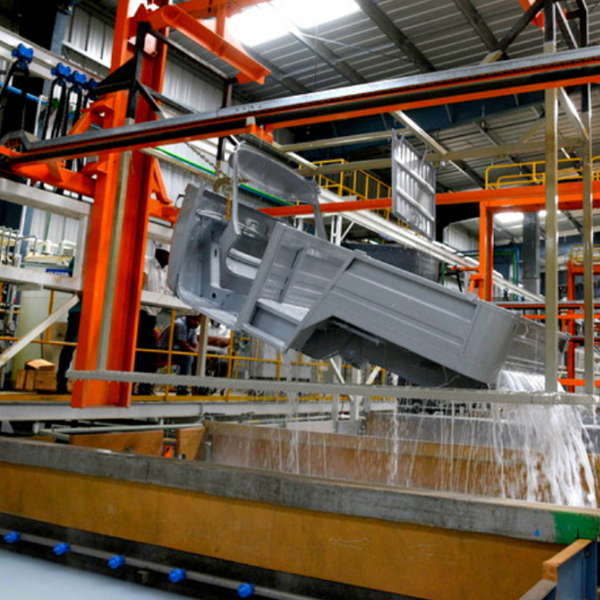
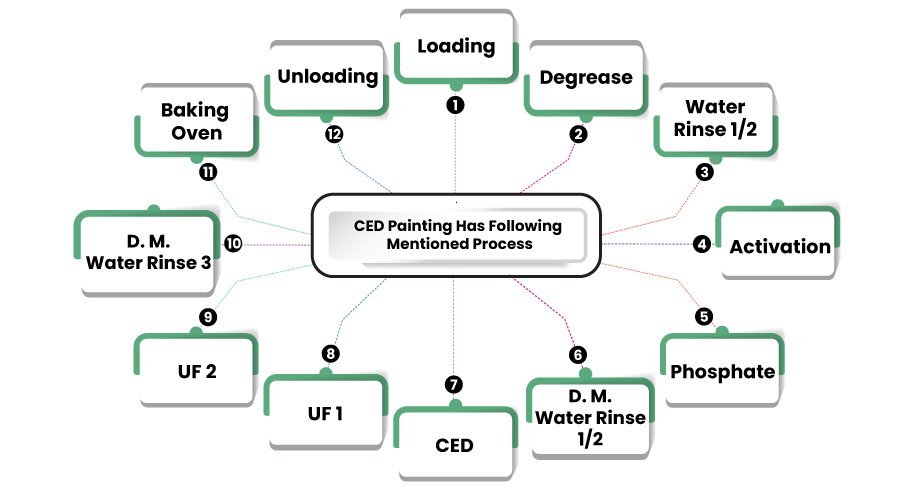
For a modern automotive paint shop, electro-deposition of primary coating has become standard. The charged components of the paint emulsion travel to anode (AED) or cathode (CED) under electrical pressures in CED (CED). The direct current created by the bath converts the paint’s pigment and resin base into the body’s surfaces. Coating is applied to all surfaces.
The deposited film does not disintegrate. The un-deposited material, on the other hand, is washed. For ED paint components, ultra-filtration (UF) technology is utilised to separate non-film and paint recovery. After stoning, the dislodged film hardens into a tough, long-lasting polymer film.
Advantages of CED Coatings
- Film Thickness Managed through Fully Automatic Operations
- Consistent Coating
- Better box and interior Surface Coverage
- Well-Covered Sharp Corners
- No Flows and Slumps
- No Solvents Boils
- Improved Chip and Corrosion Resistance
- Almost 100% Paint Used
- Superior Anti-pollution, Safety, and Health Hazards Protection
Applications of CED Coatings
Automotive
- Marine solutions
- Aerospace
- Public transportation such as trains and trams
Architecture & Construction
- Building facades
- Interiors such as stainless-steel kitchen sinks
Industry
- Wind farms
- Industrial plants
- Pipelines